What Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a devastating disease for patients and families, and is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, more than breast and prostate cancer combined (1). The two main lung cantypes are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC 80-85%), and small cell lung cancer (SCLC 15%), a more aggressive cancer when compared to NSCLC (2,3) .
Lung cancer is complexified by various histopathology (e.g. adenocarcinoma, squamous, large cell, and more) and numerous clinically meaningful biomarkers that need to be assessed to provide the best treatment or select the right trial for patients (e.g. EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and more) (4). Not to worry as at Cerba research, we got you covered with a wide range of histopathology and clinically meaningful biomarker offerings that can be detected with cutting-edge technics. Contact us to find out.
Cerba Research Lung Cancer Services
Our lung cancer specialists support the whole range of lung studies from discovery / preclinical (data not shown) to phase III registration trials and beyond. Most of our projects include specialty testing, such as, but not limited to, NGS broad-panel assays, ctDNA panels, 250+ IHC simplex and multiplex protocols, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and even NanoString®.
Our Areas Of Expertise In Lung Cancer
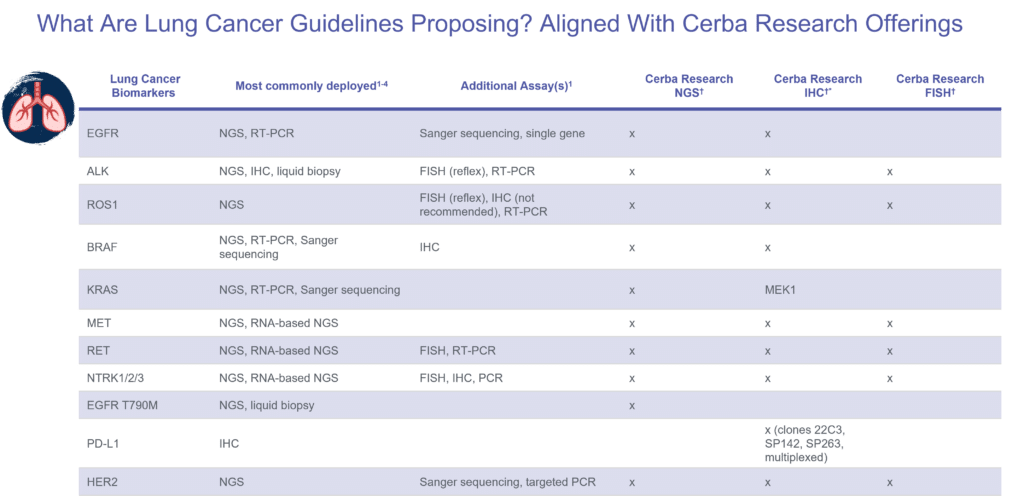
Did you know that we can cover for your lung cancer biomarker needs? Check out our mapping exercise by select lung biomarkers against our Cerba Research offerings with three technics (NGS, IHC, FISH) (4,5,6). Interested in artificial intelligence (AI) image analysis for your lung cancer trial? Check out our resources.
What Are Lung Cancer Guidelines Proposing? Aligned with Cerba Research Offerings
| Lung Cancer Biomarkers | Most Commonly Deployed | Additional Assays(s) | Cerba Research NGS | Cerba Research IHC | Cerba Research FISH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
EGFR |
NGS, RT-PCR |
Sanger Sequencing, Single Gene |
X |
X |
NA |
|
ROS1 |
NGS, IHC, Liquid Biopsy |
FISH (reflex), RT-PCR |
X |
X |
X |
| Lung Cancer Biomarkers | |
|---|---|
| Most Commonly Deployed |
NGS, RT-PCR |
| Additional Assays(s) |
Sanger Sequencing, Single Gene |
| Cerba Research NGS |
X |
| Cerba Research IHC |
X |
| Cerba Research FISH |
NA |
| Lung Cancer Biomarkers | |
|---|---|
| Most Commonly Deployed |
NGS, IHC, Liquid Biopsy |
| Additional Assays(s) |
FISH (reflex), RT-PCR |
| Cerba Research NGS |
X |
| Cerba Research IHC |
X |
| Cerba Research FISH |
X |
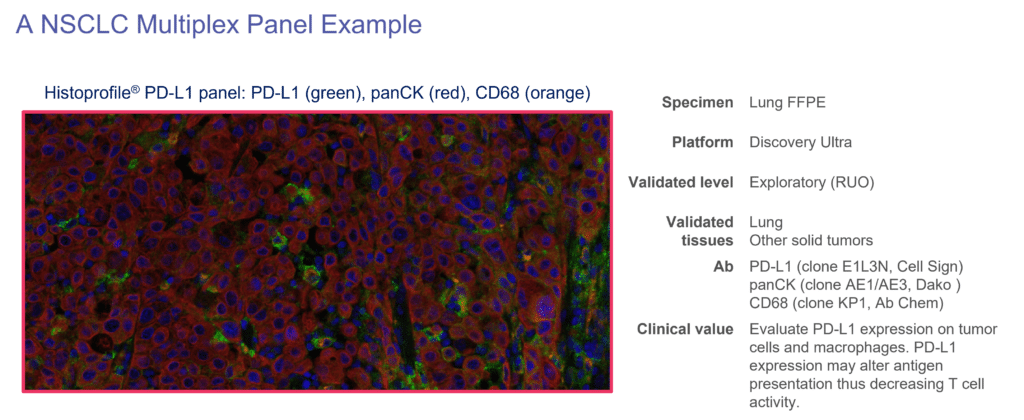
Discover Our Expertise In Transforming Research For Your Lung Cancer Treatments
We recommend starting engagement with our scientific team early, such as at the protocol design phase, for optimal results. Reach out to us here.